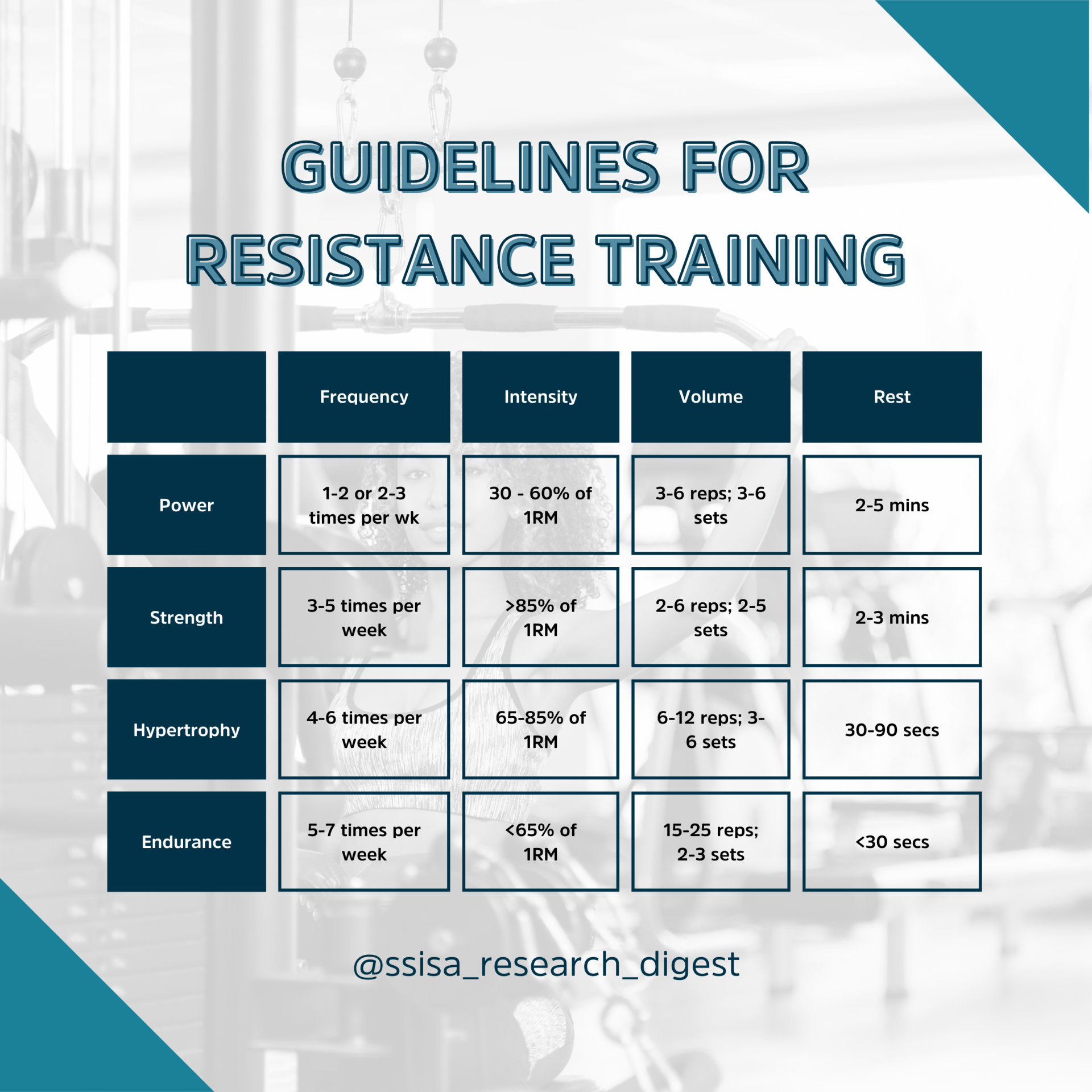
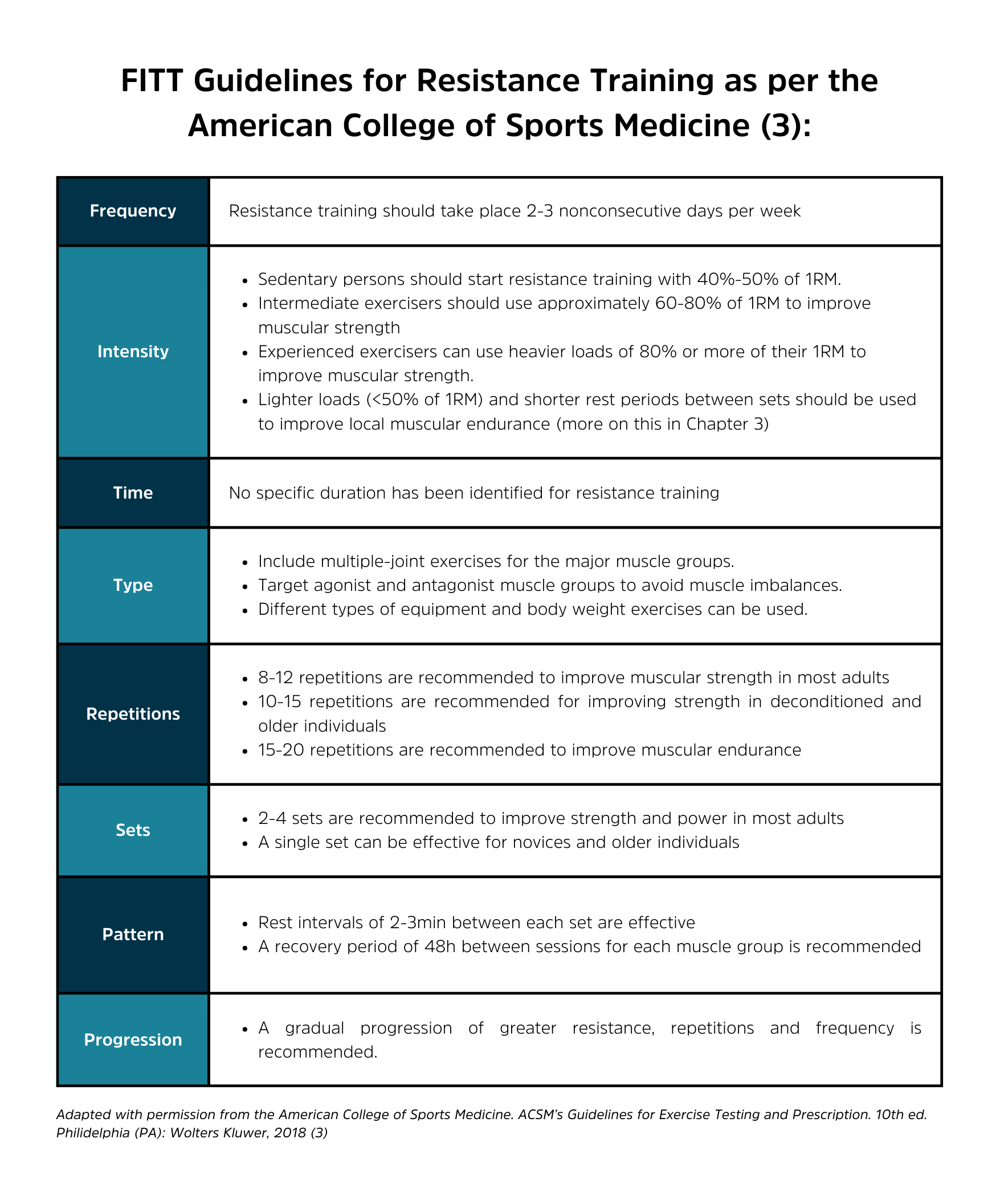
When structuring your resistance training programme, regardless of the type of resistance training approach (Muscular Endurance, Hypertrophy, Strength, Power), a few considerations need to be kept in mind, specifically the FITT-VP principle.
Generally, the FITT-VP framework is present in all forms of exercise programming. For this introduction to FITT-VP, we will focus on resistance training (RT), which is also referred to as strength training. In summary, training each major muscle group should take place 2 to 3 days per week; it is recommended that 60% to 70% of one repetition max (1RM) should be utilized to develop strength for novice to intermediate exercisers, and more experienced exercisers should adopt 80% or greater of 1RM in their programming. Regarding the development of muscular endurance, it is recommended that 50% 1RM or lower loading is used for each major muscle group across various exercises (1).
The FITT-VP principle includes the following (1):
• Frequency (how often is exercise done each week)
• Intensity (how hard is the exercise)
• Time (how long is the exercise duration)
• Type (what is the mode of exercise)
• Volume (what is the total amount of exercise)
• Progression (how is the program advanced)
Generally, the FITT-VP framework is present in all forms of exercise programming. For this introduction to FITT-VP, we will focus on resistance training (RT), which is also referred to as strength training. In summary, training each major muscle group should take place 2 to 3 days per week; it is recommended that 60% to 70% of one repetition max (1RM) should be utilized to develop strength for novice to intermediate exercisers, and more experienced exercisers should adopt 80% or greater of 1RM in their programming. Regarding the development of muscular endurance, it is recommended that 50% 1RM or lower loading is used for each major muscle group across various exercises (1).